Ekonomika ISSN 1392-1258 eISSN 2424-6166
2019, vol. 98(2), pp. 85–96 DOI: https://doi.org/10.15388/Ekon.2019.2.6
The Impact of External and Internal Factors on Strategic Management of Innovation Processes at Company Level
Oksana Shatilo*
National Transport University of Kyiv, Ukraine
Abstract. The impact of external and internal factors on organization of operation at company level is studied. The necessity for implementing strategic management of innovation processes at company level is substantiated. The structural interactions of external and internal factors on the organization of company operation are determined; a classification of factors of external and internal environment in the context of strategic management of innovation processes at company level is constructed.
Keywords: external environment, internal environment, strategic management, innovation processes, companies.
* Corresponding author:
Faculty of Economics and Law, National Transport University of Kyiv, 1 M. Omelyanovich-Pavlenko str, Kyiv, 01010, Ukraine.
Email: ov.shatilo@ukr.net
Received: 24/10/2019. Revised: 25/11/2019. Accepted: 5/12/2019
Copyright © 2019 Oksana Shatilo. Published by Vilnius University Press
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Licence, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
1. Introduction
A company exists and operates in the conditions of an external and internal environment. The internal environment of a company enables its development and operation. It can be a source of either business expansion or problems that disrupt its existence. The external environment provides a company with resources required to support its internal capacities. At company level, the factors of external and internal environment have impact on the overall operation, innovation, management decision-making. It should be noted that apart from other reasons, poor performance of companies is associated with lack of innovation processes and a mechanism for their strategic management. An important step in the company development is to identify the external and internal factors with impact on strategic management of innovation processes.
2. Literature review
Factors of the external and internal environment of the company have been the subject of research by many Ukrainian and foreign scientists. Dykan V.L., Zubenko V.O., Makovoz O.V., Tokmakova I.V., Shramenko O.V. (2003) determine two separate subsystems and give detailed description of the factors of external and internal environment. ShvetsYu.O. (2016) argues that for company development it is necessary to distinguish between the factors of external environment and internal environment with consideration to the specifics of company operation. DovhanL.Ie., KarakaiYu.V., Artemenko L.P. (2011) interpret the company environment as factors with direct and indirect impact on the company operation. Hevko O.B., Shved N.M. (2016) put emphasis on the information component as an important element in the analysis of external and internal environment; Fisunenko P.A., Lazhe M.V. (2016) consider the external and internal environment in the context of situational plans as a means of reaction on external and internal threats. Hrechan A.P. (2005) points out on the necessity to outline the innovation component in the external and internal environment. According to Fedulova L.I., Kolosh M.O. (2007) strategic management is based on analysis of both internal and external environment, with emphasis made on the external factors and management analysis to improve the company performance.
In spite of the significant stock of literary sources devoted to analysis of the factors of external and internal environment at company level, some problems are still to be elaborated, including certain aspects of these factors’ impact in the context of strategic management of innovation processes at the company level, which raises the importance of this study.
Mahmood N. (2012) builds his paper on previous theoretical and empirical studies to determine the extent to which contextual factors impact the strategic decision-making processes. Results showed that researches on contextual factors effecting the strategic decision-making process are either limited or have produced contradictory results, especially studies relating decision’s familiarity, magnitude of impact, organizational size, firm’s performance, dynamism, hostility, heterogeneity, industry, cognitive diversity, cognitive conflict, and the manager’s need for achievement to strategic decision-making processes.
Pearce J.A., Robinson R.B. Jr. (1994) determine the characteristics of strategic issues and their peculiarities in the context of external and internal factors of enterprises. Zakic N., Jovanovic A., Stamatovic M. (2008) study the influence of external and internal factors on product and business processes innovation. Marge S., Ulle P., Toomas H. (2017) indicate the factors that influence strategic management attitudes. Factor analysis is used to detect those factors affecting the internal and external environment. As a result of the study, the following potential critical success factors for the competitiveness of organisations in cultural and creative industries were mapped: the lack of financial resources, a highly competitive environment and orientation to international co-operation.
Genc E., Sengul R. (2015) investigate the theoretical background to the relationship between strategic management and organizational performance. They also identify how internal and external contextual factors have mediating and moderating effects on this relationship, and suggest that studies analysing the fit between strategic management practices and performance in public sector organizations should take the influence of contextual parameters into consideration.
Rajasekar J. (2014) proposed seven factors that affect implementation strategy. The results demonstrate that leadership is by far the most important factor influencing successful implementation strategy in enterprises. Lee C., Lee K., Pennings J. M. (2001) note that the influence on the external and internal factors of the enterprise have external networks, only the linkages to venture capital companies predicted the start-up’s performance. Several interaction terms between internal capabilities and partnership-based linkages have a statistically significant influence on performance. Sponsorship-based linkages do not have individual effects on performance but linkage with financial institutions has a multiplicative effect with technological capabilities and financial resources invested in enterprises. Kraja Y.B., Osmani E. (2015) show the importance of external and internal factors in the creation of the SME’s competitive advantage.
Rajasekar J. (2014) argues that the body of knowledge in this area is rich with surveys and industry-based studies. Factors that affect strategy implementation can be categorized as leadership style, information availability and accuracy, uncertainty, organizational structure, organizational culture, human resources, and technology. Although most authors agree that these factors affect strategy implementation, each factor’s impact is at a different level and carries a different force. (Lorange, 1998) stated that human resources are becoming the key focus of strategy implementation and reiterated that people, not financial resources, are the key strategic resources in strategy implementation. In a study involving 172 Slovenian companies, Cater and Pucko (2008) demonstrated that managers mostly rely on planning and organizing activities when implementing strategies, while the biggest obstacle to strategy implementation and execution is poor leadership. Their results showed that adapting the organizational structure to serve the execution of strategy has a positive influence on performance. Fulmer (1990) mentioned that human resources management plays an important role in the effective implementation of strategic plans. It is important for both organization departments and employees to be enthusiastic about the strategy implementation. Getting people involved and having a motivating reward system will have a positive influence on the implementation of a strategy.
Indris S., Primiana I. (2015) determine the influence of internal and external environment analysis on the performance of small and medium companies.
Griffiths W., Webster E. (2010) give evidence suggesting that most of a firm’s R&D activity can be explained by time-invariant factors, which we believe relate to internal and specific characteristics such as the firm’s managerial dimensions, competitive strategy, and how it communicates with employees. Of the remaining time-varying portion, we find that past profits, the rate of growth of the industry and the level of R&D activity over the firm’s industry is pertinent. These results are suggestive, since we cannot clearly identify the extent to which the firm’s internal behaviour is conditioned by its external environment.
3. Results of the Research
The company development in the market conditions depends on its quick response on the changing consumer needs and its capacity to adapt to them. An important factor of the company advancement is strategic management of innovation processes, which constitutes a set of objectives and tasks focused on implementation of new approaches, methods and management systems by exploiting its internal resource capacities.
The need for strategic management of innovation processes at the company level is determined by their critical role in the economic development of a country. Company management has to set the objectives focused at competitiveness enhancement: creation or modernization of technical facilities for production of goods/services, introduction of innovative approaches to organization of production and professional development of staff etc. Innovation processes at the company level are designed to increase the efficiency fixed assets or cost reduction, which enables to increase its profit and, ultimately, its competitiveness. Any measures aiming to optimize company operation, including ones related with innovating, need due consideration for external and internal factors with impact on the company performance.
Because the factors of external and internal environment have effects on various aspects of company operation, including innovation, a company not only needs to adapt to its external environment, but also improve its internal structure from which threats and opportunities for its development originate. These factors need to be outlined considering the specifics of strategic management of innovation processes when analyzing the researchers’ views.
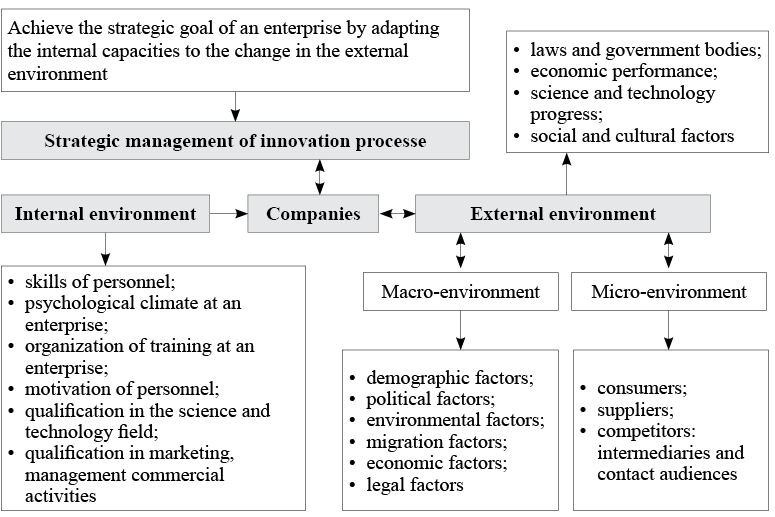
According to Dovhan L. Ye., Karakai Yu. V., Artemenko L. P.(2011), the external environment is one that has indirect impact (laws and government bodies, economic performance, social and cultural factors, environmental factors, science and technology progress, international events) on a company, and direct impact on it (competitors, consumers, contact audiences, partners, resource suppliers).
At the same time, Dykan V.L., Zubenko V.O., Makovoz O.V., Tokmakova I.V., Shramenko O.V. (2013) consider the external environment as a set of two relatively autonomous subsystems: macro-environment and micro-environment. The factors of micro-environment are consumers (the level and evolution of consumer demand for goods and the market development); suppliers (attractiveness of suppliers, reasonability of contract policy); competitors (numbers of competitors, their activity and the overall state of competition): intermediaries and contact audiences. The factors of macro-environment include:
• economic factors: change in the monetary and non-monetary incomes of the population, amount of salaries; pensions, inflation, performance and trends of the domestic industries, the development international economic relations;
• political factors: the political stability in a country and a region, vectors of the political system development;
• legal factors: the impact of the legal framework on business activities, methods for business regulation, the government’s attitude to small business;
• demographic factors: characterized by the overall number of the population;
• natural factors: environmental performance in a country or a region;
• social and cultural factors: the public welfare;
• factors of the science and technology progress.
The similar views are held by Hevko O.B., Shveda N.M. (2016), who argue that nowadays the existing information systems offer company managers the information with focus on and detailed description of the internal environment parameters (technology, organization of production, retrospective series on financial and economic performance). But information on external environment is fragmented and irregular. There is no information on economic tendencies, science and technology achievements, markets and competitions on them, consumers and their needs. Moreover, there is lack of social and political information: its collection and analysis is not adequately performed even in research institutes. The abovementioned causes the prevalence of subjective ideas about the situation at an enterprise and outside it, not allowing for constructing sound forecasts and taking strategic decisions.
Shvets Yu.O. (2011) believes that the factors of the external and internal environment need to be classified as general and specific ones, with the latter including the specifics of the process involved in the use and management of the current assets. These factors enable for a better understanding of the goals, for creating jobs and social guarantees for personnel, opportunities for taking part on profit sharing, for exercising control over the output and sales, for monitoring the flows of current assets and the duration of financial and operation cycle. Once the above factors of external environment are analyzed, they need to be taken into account in business planning, economic activity selection, strategy building, setting relations with other enterprises and government; positive effects of these factors should be used and negative effects mitigated, with turning the threats and signs of crisis situations into opportunities for future development.
Fisunenko P.A. and Lazhe M.V. (2016) make an analysis of the external environment that lays the basis for macroeconomic, socio-political, production, and technological forecasts, and can be used for assessing the long-term capabilities of an enterprise in the conditions of the predictable development of involved processes. Predictions of threats and favorable possibilities is a determinant for the timely making of situational plans for the occasion of their occurrence, which simplifies building a strategy that would enable an enterprise to achieve the goals and turn adverse circumstances into good conditions for operation. The current external environment of enterprises features the extremely high level of complexity, dynamics and uncertainty. The ability to adapt to the change in the external environments is the most essential conditions in business and other walks of life. Moreover, it is a condition of survival and development.
It is, therefore, important to note that, on the one hand, enterprises need be constantly aware of the new character of change in the environment and be able to effectively react on them. On the other hand, one has to be aware that enterprises themselves generate changes in the external environment by producing new types of goods and services, using new types of raw materials, equipments and technologies.
As argued by Hrechan A.P. (2005), for the development of an enterprise, due consideration needs to be given to external factors (opportunities for producing new or improved types of products or services; opportunities for changing social relations at an enterprise (personnel innovations); opportunities for developing new management methods (management innovations); opportunities for creating new mechanisms for market promotion of products (market innovations); opportunities for purchasing know-how, patents; legal framework, low rate of re-financing, privileged taxation; interactions of government and business; practice of technology commercialization etc.), and internal factors (the receptivity of an enterprise to innovations, the experience of launching new projects, policy of the management in innovation, the attitude of personnel to innovations).
Such an approach can bring to life a new product or a new service, with which an enterprise will be able to enter new international markets, develop diversification, perform commercial triangulation, set up new technology training for personnel and, in the final end, to increase its profits.
Fedulova L.І. (2007) proposed a classification, where the internal factors include internal resources creating the innovation capacities, namely: skills of employees, qualification in marketing and commercial activities, psychological climate, organization of professional training, motivation of employees, science and technology competencies, external economic relations, patent and legal issues. External factors are as follows: internal market demand, taxes, relations with large enterprises and customers, supplies of materials and components, financing, lending, standardization and certification, access to government orders, author’s supervision of projects, external market demand, intellectual property protection, market of patents and services, operation of innovation infrastructure outside an enterprise, risk insurance. Apart from this, the author deems it important to form another group, including in it the capacities enabling an enterprise to innovate, namely: technical level of equipment, implementation of science and technology developments, organization of production, trial and experimental production facilities, participation in exhibitions, distribution of products, seeking to launch production of new products, compliance of the organization’s structure with the needs in its innovation activities, adequate information support, certification of products, marketing studies, search for investors, information support for innovative developments, expert review of projects, finding solutions for problems of intellectual property protection in Ukraine, search for patents and patenting abroad.
According to Zakic N., Jovanovic A., Stamatovic M. (2008), there are some more factors that have to be considered. Some of important outer factors that are not included in the analysis are the influence of outer stakeholders and institutional environment. Inner factors that can be the subject of analysis include the personality, orientation and attitudes of relevant innovation decision-makers (owners/managers), availability of resources, costs, etc.
A literature review of Mahmood N. (2012), pertaining to external environmental factors reveals certain important gaps. Most of previous studies have focused on one aspect of the external characteristics (e.g. stability). Factors such as hostility, velocity, heterogeneity, and uncertainty have received relatively little attention while researches relating to environmental dynamism and hostility to strategic decision-making process have produced contradictory results. As regards the environmental factors that influence strategic decision-making process, the dimensions of dynamism, hostility, heterogeneity, and stability were found to be significant.
Marge S., Ulle P., Toomas H. (2017) show that enterprises also face the following challenges in their daily activities: being innovative, making profit, having no confidence in terms of income, receiving external funding, finding customers and obtaining new orders. Second, enterprises are driven to think and act strategically by three closely linked factors: a challenging environment, willingness to increase international competitiveness, and willingness to expand to foreign markets. However, organizations that think and act strategically barely face any challenges – internal or external. It is also important to stress that they are also coping well with their finances.
According to Pearce II & Robinson (1994), strategic issues typically have the following characteristics:
• require large amount of the firm’s resources,
• often affect the firm’s long term prosperity,
• they are future-oriented,
• usually have multifunctional consequences,
• they require consideration of the firm’s external environment, and
• require top-management decisions.
Genc E., Sengul R. (2015) demonstrate that the rational strategic management is constructed upon a body of rules in a top-down structural hierarchy. Central government strategies, as an external influencer, may therefore potentially affect organizational performance in financial terms. For example, the Meier et. al. (2007) study of Texas School Districts reveals that organizations need central support in order to maximise their performance. Despite the traditional prominence of the rational approach to strategising, there is an important body of work that considers the value of an approach at the other end of the spectrum – incremental approach. This enhances the role of organizations’ members, viewing them as active participants in the development and implementation stages, something encouraged by the incremental approach. Although staff participation, as an internal factor, it is considered to improve organizational performance, the separation of formulation and implementation stages may provoke the failure of the overall strategy. This study provides several theoretical and practical implications for researchers and managers who are concerned with new business ventures. First of all, this study confirmed (showed) the importance of financial capital invested and technological capabilities. Financial resources invested are as important as technological resources in determining organizational performance in the context of new business ventures.
Kraja Y., Osmani E. (2015) divide the environmental factors in the following way (Table 1).
Table 1. Factors of external and internal environment
|
External environment |
Internal environment |
|
1. The main force that influence the competition in your company is the rivalry among the existing competitors. 2. The main force that influence the competition in your company is the bargaining power of buyers. 3 The main force that influence the competiton in your company is the bargaining power of suppliers. 4. The main force that influence the competition in your company is the risk by the new entrances. 5. The main force that influences the competition in your company is the threat of substitutes. |
1. The capabilities to create the qualitative products and services. 2. Distinctive competencies to assess and to transmit knowledge. 3. Capabilities to communicate values and goals. 4. Trust and brand names of the firms. 5. The abilities to evaluate and use the culture. 6. Capabilities to manage the human resources. 7. Capability to use technologies. 8. Capabilities, skills, trainings and experience at work. 9. Abilities to use software. 10. Capabilities to generate business plans and to clarify that how ideas can be turned in reality. 11. Skills to analyze and to forecast new possibilities. 13. The impact of the tangible assets. |
Indris S., Primiana I. (2015) put forward two hypotheses that affect the external and internal environment: hypothesis 1: the performance of small and medium industries (SMEs) influence by internal environment analysis; hypothesis 2: the performance of small and medium industries (SMEs) influence by external environment analysis.
The results of Griffiths W., Webster E. (2010) have implications mainly for corporate policy. They suggest that being innovative is a long-term strategy involving certain managerial dimensions, an extensive use of communication techniques and practices to prevent absorption. There is a need to examine how policy makers can engineer more appropriate managerial behaviour. It may involve new ways to engage existing managers, other than the current suite of conferences and meetings that are popular, or it may involve attracting a different calibre of person into the ranks of management.
The above review of literary sources enables us to determine the structural interactions of the impact of external and internal factors on the organization of operation at company level, and to construct a classification of factors of external and internal environment in the context of strategic management of innovation processes at the company level (see Figures 1 and 2).
All the factors that affect the effectiveness of business management are interrelated and raise a number of topical issues that should be addressed:
• raising the level of income of enterprises, both by increasing profits, optimizing production processes and reducing costs;
• improvement of unsatisfactory condition of fixed assets of enterprises;
• increasing the adaptability of the enterprise to the influence of environmental factors;
• increase of financial stability and independence of the enterprise;
• improving the quality of products or services
• increasing the level of use of innovation in the activity.
Solving a number of existing enterprise problems is possible by improving the efficiency of management. That is why there is an objective need to analyze the current state of enterprise management effectiveness as a result of the influence of factors.
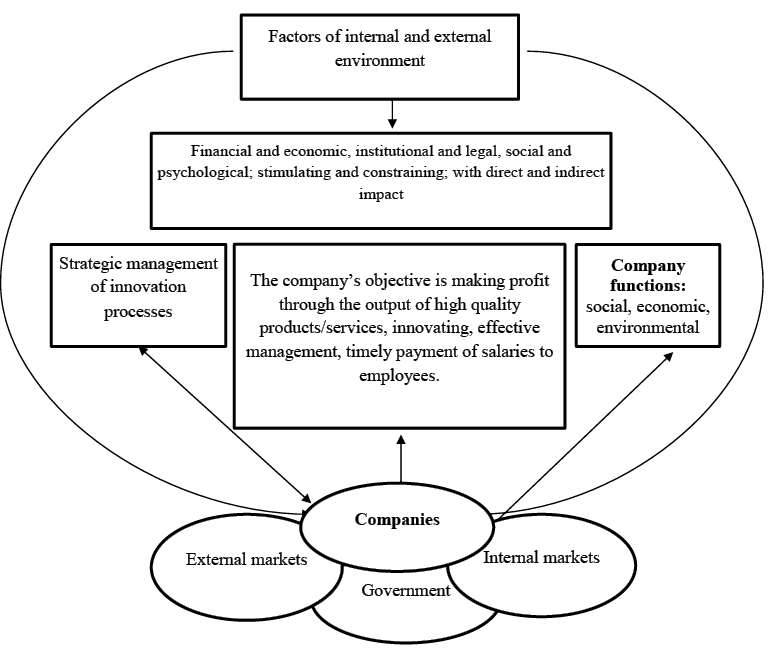
Fig. 1. The structural interactions of the impact of external and internal factors on the organization of operation at company level.
Source: constructed by the author by use of [Hevko O.B., Shveda N.M. (2016); FisunenkoP. А., Lazhe M.V. (2016); Mahmood N. (2012); Zakiс N., Jovanoviс A., Stamatoviс M.(2008); Fedulova L.І., Kolosh M.O. (2007); Lorange, P. (1998)].
The practical use of the constructed classification (see Figure 2) is that it will allow company managers to identify and measure the factors with most significant positive effects for innovation when elaborating the strategy for management of innovation processes as part of the overall optimization of company management.
Fig. 2. A classification of factors of external and internal environment in the context of strategic management of innovation processes at company level.
Source: developed by the author using the data from [Dovhan L. Ye., KarakaiYu. V., Artemenko L. P. (2011); Marge S., Ulle P., Toomas H. (2017); Hrechan А.P. (2005); Pucko, D., Cater, T. (2008); Lee C., Lee, K., Pennings, J. M. (2001); Fedulova L.І., Kolosh M.O. (2007); Rajasekar J. (2014); Lorange, P. (1998); Fulmer, W.E. (1990)].
These factors allow you to better understand the goals you create, the jobs and social guarantees for staff to create the opportunity to participate in the distribution profit, control the volume of products produced and sold, determine availability of working capital, duration of financial and operating cycle. In turn, the formed environmental factors must be taken to attention when planning directions, choosing a field of activity, developing a strategy, establishing relationships with businesses and the state, and uniting the positive and negative manifestations of these factors, turn threats and signs of crisis into favorable future development opportunities.
So, in spite of the varying approaches to determining and analysis of the company environment, the algorithm of the analysis contains standard phases: identifying the external and internal factors with direct impact on company operation; collecting the data required for analysis; analysis and summing up its results.
The models of external and internal environment considered do not exhaust the full diversity of existing approaches, but show the most significant directions in this matter. The practical value of these models is different for different sectors of the economy and enterprises. Today, there is no single, integrated approach to building a general concept of strategic management of the external and internal environment that would comprehensively combine economic, technological, social and political influences on the enterprise, features of interaction of the enterprise with its partners, competitors, consumers, etc. However, there is already a general trend in strategic analysis.
4. Conclusion
It is worth noting that the study of the internal and external environment of the enterprise allow you to determine its competitive position the position that the company occupies in your industry, to a particular market segment, according to your performance and your own advantages and disadvantages compared to other enterprises
Strategic management of innovation processes cannot be implemented without due consideration for external and internal factors with impact on company operation. A review of literary sources enables to determine the structural interactions of the impact of external and internal factors on the organization of operation at company level are determined, and construct a classification of the factors of external and internal environment in the context of strategic management at company level. The can be useful for company managers in analyzing the resource efficiency, improving labor system, proposing innovative goods/services and technologies.
References
Dykan V.L., Zubenko V.O., Makovoz O.V., Tokmakova I.V. & Shramenko O.V. (2013). Strategic management. Kyiv: Center of education literature.
Dovhan L. Ye., Karakai Yu. V. & Artemenko L. P. (2011). Strategic management. 2nd edition. Kyiv: Center of education literature.
Fedulova L.І. & Kolosh M.O. (2007). The innovation capacities of an enterprise: a factor for the efficiency of restructuring. Scientific works of Interregional Academy of Personnel Management, 3, 48-56. http://jeou.donnu.edu.ua/article/view/1054/1072.
Fisunenko P. А. & Lazhe M.V. (2016). Analysis of the factors of external and internal environment for construction enterprises, with impact on the economic security. Business Inform, 10, 189–195. http://nbuv.gov.ua/UJRN/binf_2016_10_29.
Genc E. & Sengul R. (2015) A Review on the Relationship Between Strategic Management and Performance: The Role of Internal and External Contexts. Strategic Public Management Journal (SPMJ), 2, 56-71. https://dergipark.org.tr/en/download/article-file/274021.
Griffiths W. & Webster E. (2010) What governs firm-level R&D: Internal or external factors? Technovation 30, 471–481. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.687.8087&rep=rep1&type=pdf.
Hevko O.B, & Shveda N.M. (2016). Strategic management. Tutorial. For students of all forms of study direction 6.030601 “Management” Ternopil: FOP Palyanitsa V.A., 2016. - 152 p.
Hrechan, А.P. (2005). The teoretical foundations for determining the innovation capacities of an enterpise. The economy and the state, 7, 34–37. https://scholar.google.com.ua/scholar?hl=ru&as_sdt=0,5&cluster=14615790171306777720.
Indris S. & Primiana I. (2015) Internal and External Environment Analysis on the Performance of Small and Medium Industries (SMES) In Indonesia. International journal of scientific & technology research, 4(4), 188-196. https://www.ijstr.org/final-print/apr2015/Internal-And-External-Environment-Analysis-On-The-Performance-Of-Small-And-Medium-Industries-smes-In-Indonesia.pdf.
Kraja Y.B. & Osmani E. (2015) Importance of external and internal environment in creation of competitive advantage to SMES. (case of SMES, in the or then region of Albania) European Scientific Journal edition, l.11(13), 120-130. https://eujournal.org/index.php/esj/article/view/5641/5467.
Lorange, P. (1998). Strategy implementation: the new realities. Long Range Planning, 31(1), p. 18-29, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0024630197000873.
Lee C., Lee, K. & Pennings, J. M. (2001). Internal Capabilities, External Networks, and Performance: A Study on Technology-Based Ventures. Strategic Management Journal, 22(6-7), 615-640. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/smj.181.
Mahmood, N. (2012) Factors Influencing Strategic Decision-Making Processes. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Science, 2(7), 405-429. http://hrmars.com/admin/pics/985.pdf.
Marge S., Ulle P. & Toomas H. (2017) Factors affecting strategic management attitudes and practices in creative industries organisations. Encatc journal of cultural management &policy, 7(1), 71-87. https://www.encatc.org/media/3723-6_encact-vol-7_marge-sassi_ulle-pihlak-toomas-haldma.pdf.
Rajasekar, J. (2014) Factors affecting Effective Strategy Implementation in a Service Industry: A Study of Electricity Distribution Companies in the Sultanate of Oman. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 5(9(1)), 169-183, http://ijbssnet.com/journals/Vol_5_No_9_1_August_2014/15.pdf
Pearce, J.A. II & Robinson, R.B. Jr. (1994). Strategic Management, Formulation, Implementation, and Control, 5th ed. Burr Ridge, Illinois: Irwin inc..
Pucko, D., & Cater, T. (2008). A holistic strategy implementation model based on the experiences of Slovenian companies. Economic and Business Review for Central and South – Eastern Europe, 10(4), 307-325. http://www.ijil.ui.ac.id/index.php/tseajm/article/viewFile/1042/958.
Shvets, Yu.O. (2016). The impact of the factors of external and internal environment on the effectiveness of strategic management of current assets in mechanical engineering enterprises. Bulletin of Zaporizhzhya National University Economics, 1 (29), 26–36, http://nbuv.gov.ua/UJRN/Vznu_eco_2016_1_5.
Zakiс N., Jovanoviс A. & Stamatoviс M. (2008) External and internal factors аffеcting the product and business process innovation. Facta Universitatis Series: Economics and Organization, 5 (1), 17 – 29. http://facta.junis.ni.ac.rs/eao/eao200801/eao200801-03.pdf